
ECS Return Charges Explained: A Comprehensive Guide for Indian Investors
In today’s fast-paced financial ecosystem, automation plays a significant role in streamlining monetary transactions. The Electronic Clearing Service (ECS) has emerged as a reliable system for automating recurring payments such as loan EMIs, SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans), mutual fund installments, and more. However, the flipside of convenience arises when an ECS transaction fails, leading to ECS return charges.
For Indian investors and borrowers, understanding ECS return charges and learning how to avoid them is crucial. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know, using clear insights to enhance your financial awareness.
What Are ECS Return Charges?
ECS return charges are fees levied by banks or financial institutions when an ECS transaction is unsuccessful. Such failures typically occur due to insufficient account balances, incorrect account details, or non-business days. In India, ECS is commonly used for:
- Paying loan EMIs.
- Automating SIP and STP (Systematic Transfer Plans) in mutual funds.
- Clearing utility bills, insurance premiums, or credit card payments.
When an ECS transaction fails, the bank or institution charges a penalty to cover processing costs. These charges vary between financial institutions but generally range between ₹200 and ₹500 per failed transaction, depending on the type and terms of the transaction.
The Impact of ECS Return Charges
While the monetary penalty might appear small initially, ECS return charges can disrupt your financial stability and long-term plans. Here’s how:
- Interrupted Investment Growth
- Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs) thrive on consistency. A single missed SIP due to ECS failure can disrupt the compounding benefits of your investment, derailing financial goals.
- Lower Creditworthiness
- Repeated ECS failures could negatively affect your credit score in India. For individuals reliant on credit cards, loans, or future borrowings, this can prove costly.
- Added Financial Stress
- Multiple ECS failures, compounded by penalties and missed deadlines, may lead to unnecessary financial stress and additional charges, such as late payment fees.
Common Causes of ECS Returns in India
Identifying why ECS transactions fail is the first step to preventing such occurrences. Below are some of the most common reasons:
1. Insufficient Account Balance
- In India, many individuals overlook maintaining adequate funds in their accounts, especially if they rely on manual transfers to meet ECS commitments. This oversight often leads to ECS returns.
2. Incorrect Account Details
- Any mismatch or outdated account information provided during the ECS setup process can trigger transaction failures.
3. Bank Holidays
- Transactions scheduled on national or regional bank holidays in India may fail due to operational delays or holiday closures.
4. Mandate Issues
- A failure to renew or update ECS mandates in time can result in unauthorized or invalid transaction attempts.
5. Technical Errors
- Network or server issues on either the bank’s or the fund house’s side can occasionally lead to failed transactions.
How to Avoid ECS Return Charges
Here’s a practical roadmap to avoid ECS return charges while ensuring smooth financial transactions:
1. Maintain a Minimum Account Balance
- Always ensure your bank account has sufficient funds to honor ECS payments. A good practice is to set reminders for upcoming SIPs or EMIs to avoid insufficient funds.
2. Double-Check Account Details
- Verify your bank account number, IFSC code, and other mandate details before submitting ECS instructions. Keep these updated in case of any changes.
3. Be Mindful of Bank Holidays
- In India, where regional and national holidays vary, consider scheduling ECS payments a day or two before the due date to avoid potential disruptions.
4. Enable Alerts and Notifications
- Activate SMS and email notifications for your bank account. These will alert you to low balances or scheduled ECS payments, ensuring timely corrective actions.
5. Review Your ECS Mandates Regularly
- ECS mandates typically have a validity period. Periodically check and renew mandates to avoid lapses that could result in transaction failures.
6. Leverage Auto-Debit Features
- Modern banking apps in India often come with auto-debit functionality, allowing you to automate fund transfers well in advance of the ECS schedule.
ECS Return Charges Across Indian Banks
Different banks in India charge varying fees for ECS returns. Below is a general comparison:
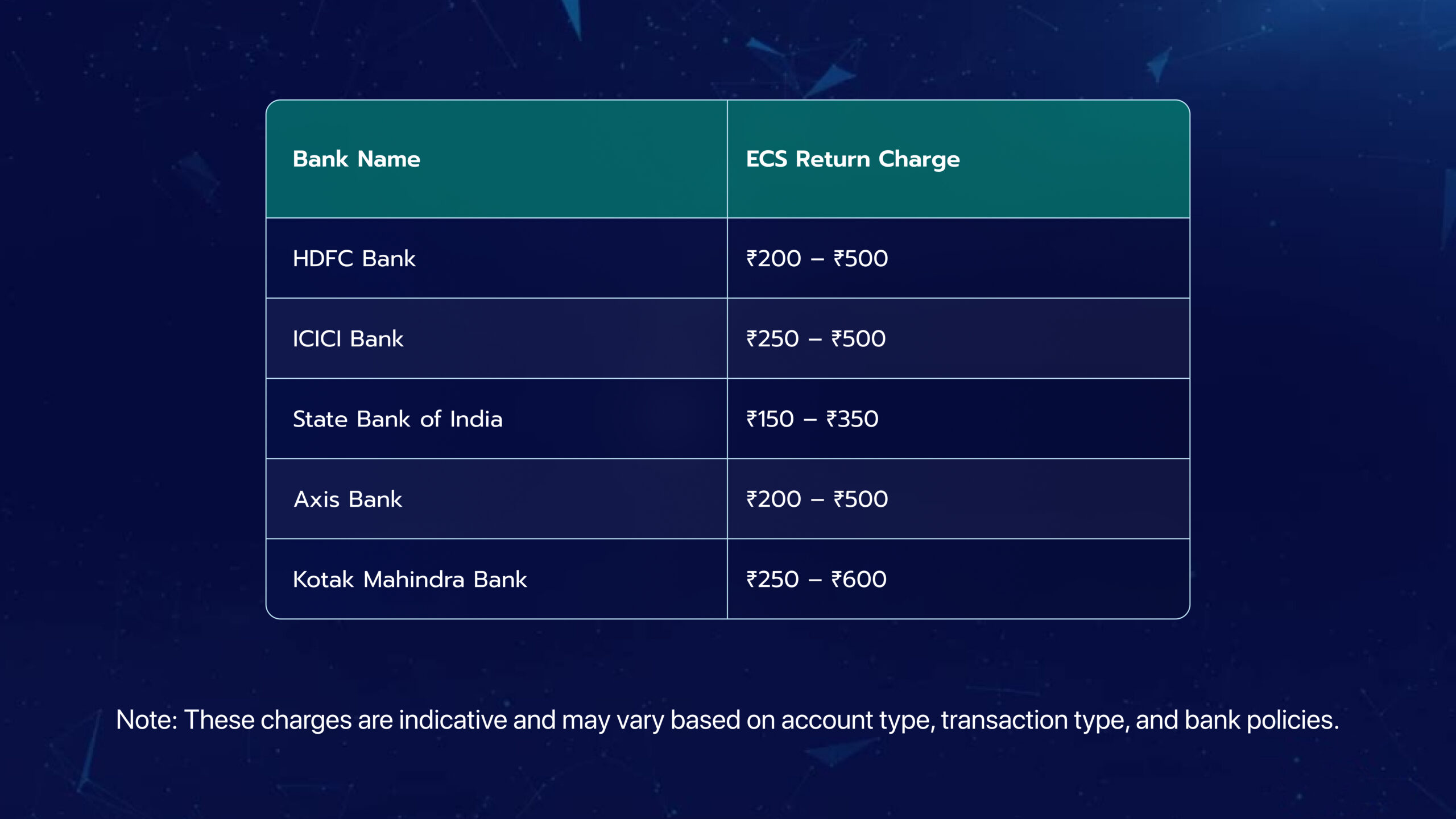
ECS in Mutual Funds and SIPs
Mutual funds are one of the most common use cases for ECS in India, particularly for automating SIPs. Regular investments are key to wealth creation, and an ECS return can disrupt this process. To avoid SIP failures:
- Keep an Investment Buffer: Always maintain a balance slightly higher than the SIP amount in your account.
- Choose a Convenient SIP Date: Select a date that aligns with your salary credit or income inflows.
- Set Up a Backup Payment Method: Link a secondary account to your SIP for emergencies.
Digital Alternatives to ECS in India
The emergence of UPI (Unified Payments Interface) and other digital platforms has offered Indians more flexible payment methods, reducing the dependency on ECS. For recurring payments:
- Use UPI autopay for a seamless alternative to ECS.
- Opt for credit card-linked auto-pay for bills or EMIs.
- Explore banking apps that allow customizable payment schedules.
Steps to Resolve ECS Failures
If an ECS transaction fails, act swiftly:
- Contact Your Bank Immediately
- Enquire about the cause of the failure and resolve any underlying issues, such as low balance or incorrect details.
- Check Your Mandate Status
- Ensure your ECS mandate is active and valid.
- Pay Pending Dues Manually
- To avoid further penalties, clear pending payments via NEFT, UPI, or net banking.
- Review Upcoming Transactions
- Adjust your fund allocation or mandate details to prevent future failures.
Types of ECS Services in India
The Electronic Clearing Service (ECS) is a system that facilitates bulk electronic transactions, primarily categorized into two types:
1. ECS Credit
ECS Credit is used by organizations to transfer funds to multiple beneficiaries simultaneously. This system ensures timely and error-free payments, making it an efficient choice for bulk transactions.
Examples include:
- Salary disbursements: Companies deposit monthly salaries directly into employees’ bank accounts.
- Dividend payouts: Shareholders receive dividends automatically, avoiding delays.
- Pension fund transfers: Pensioners get their monthly pensions credited without manual intervention.
ECS Credit simplifies large-scale fund distribution, ensuring accuracy and promptness.
2. ECS Debit
ECS Debit allows institutions to collect recurring payments from customers automatically. This system is commonly used for regular payment collections.
Examples include:
- Loan EMIs: Banks deduct monthly installments directly from borrowers’ accounts.
- Insurance premiums: Regular policy premiums are collected without lapses.
- Utility bills: Electricity, water, or phone bills are paid on time via auto-debit.
Both ECS Credit and ECS Debit help streamline transactions, reduce manual processes, and ensure consistency in financial operations, benefiting individuals and institutions alike.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What happens when an ECS transaction fails?
When an ECS fails, the bank charges a penalty, and the transaction amount remains unpaid. It may also lead to late fees and a dent in your credit score.
2. Can ECS charges be refunded?
ECS return charges are typically non-refundable. However, in rare cases of technical errors, banks may reverse the charges upon investigation.
3. Are ECS transactions secure in India?
Yes, ECS transactions are encrypted and highly secure. However, ensure that your account details are accurate and mandates are updated regularly.
4. What are the alternatives to ECS in India?
Digital options like UPI autopay, NEFT, and RTGS offer flexible alternatives to ECS.
5. How can I check if my ECS mandate is active?
You can verify ECS mandates through your bank’s net banking portal or by visiting your bank branch.
Conclusion
ECS is a critical tool for managing recurring payments in India, especially for investments and loans. However, ECS return charges can become a financial burden if not managed proactively. By maintaining a buffer account balance, staying mindful of mandate updates, and leveraging modern payment tools like UPI, you can ensure a seamless financial experience.
Understanding ECS return charges not only saves money but also enhances your creditworthiness and investment consistency. With these tips, you’re now equipped to handle ECS payments like a pro and focus on achieving your financial goals.
Get FREE Eligibility Report
Instantly check your eligibility for Loan Against Mutual Funds
- No Minimum CIBIL Required
- 100% Digital
- 4 Working hour disbursal
Looking for Loan Against Stocks?
Recent Articles
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about loans against mutual funds in India, including benefits, eligibility criteria, interest rates, risks, the application process, and frequently asked questions.
This guide provides a comprehensive view of NSE and BSE stock market holidays for 2025, highlighting opportunities for long weekends and essential details for every trader. Use this resource to check if the Indian stock market is open today, plan for share market holidays tomorrow, or get insights into market closures throughout the year.
For Indian investors and borrowers, understanding ECS return charges and learning how to avoid them is crucial. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know


